Table Of Contents
Bezier Example(翻訳済み)¶
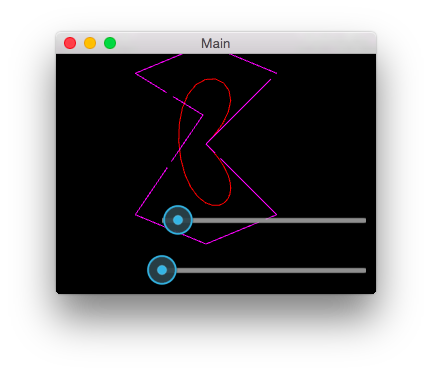
この例では多角形から計算され閉じたベジェ曲線を表示しています。 あなたは紫色のポリゴン(多角形)とポリゴンから計算された赤色のベジェ曲線、および2つのスライダが表示されます。 曲線を再計算するポリゴン上の点をドラッグできます。2つのスライダーは、2つの形状を構成する破線のダッシュの長さを制御します。
File canvas\bezier.py¶
'''
Bezier Example
==============
This example shows a closed Bezier curve computed from a polygon. You
should see a purple polygon, a red bezier curve computed from the polygon,
and two sliders. You can drag points on the polygon to recompute the curve.
The two sliders control the dash length of the dashed lines making up the two
shapes.
'''
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.floatlayout import FloatLayout
from kivy.uix.slider import Slider
from kivy.graphics import Color, Bezier, Line
class BezierTest(FloatLayout):
def __init__(self, points=[], loop=False, *args, **kwargs):
super(BezierTest, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.d = 10 # pixel tolerance when clicking on a point
self.points = points
self.loop = loop
self.current_point = None # index of point being dragged
with self.canvas:
Color(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
self.bezier = Bezier(
points=self.points,
segments=150,
loop=self.loop,
dash_length=100,
dash_offset=10)
Color(1.0, 0.0, 1.0)
self.line = Line(
points=self.points + self.points[:2],
dash_offset=10,
dash_length=100)
s = Slider(y=0, pos_hint={'x': .3}, size_hint=(.7, None), height=50)
s.bind(value=self._set_bezier_dash_offset)
self.add_widget(s)
s = Slider(y=50, pos_hint={'x': .3}, size_hint=(.7, None), height=50)
s.bind(value=self._set_line_dash_offset)
self.add_widget(s)
def _set_bezier_dash_offset(self, instance, value):
# effect to reduce length while increase offset
self.bezier.dash_length = 100 - value
self.bezier.dash_offset = value
def _set_line_dash_offset(self, instance, value):
# effect to reduce length while increase offset
self.line.dash_length = 100 - value
self.line.dash_offset = value
def on_touch_down(self, touch):
if self.collide_point(touch.pos[0], touch.pos[1]):
for i, p in enumerate(list(zip(self.points[::2],
self.points[1::2]))):
if (abs(touch.pos[0] - self.pos[0] - p[0]) < self.d and
abs(touch.pos[1] - self.pos[1] - p[1]) < self.d):
self.current_point = i + 1
return True
return super(BezierTest, self).on_touch_down(touch)
def on_touch_up(self, touch):
if self.collide_point(touch.pos[0], touch.pos[1]):
if self.current_point:
self.current_point = None
return True
return super(BezierTest, self).on_touch_up(touch)
def on_touch_move(self, touch):
if self.collide_point(touch.pos[0], touch.pos[1]):
c = self.current_point
if c:
self.points[(c - 1) * 2] = touch.pos[0] - self.pos[0]
self.points[(c - 1) * 2 + 1] = touch.pos[1] - self.pos[1]
self.bezier.points = self.points
self.line.points = self.points + self.points[:2]
return True
return super(BezierTest, self).on_touch_move(touch)
class Main(App):
def build(self):
from math import cos, sin, radians
x = y = 150
z = 100
# Pacman !
points = [x, y]
for i in range(45, 360, 45):
i = radians(i)
points.extend([x + cos(i) * z, y + sin(i) * z])
return BezierTest(points=points, loop=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
Main().run()